Why Dns Use Tcp And Udp DNS uses both TCP and UDP ports to maintain consistent and reliable network performance TCP provides zone transfers while UDP handles name resolution queries and responses When managing network ports most
When a client doesn t receive a response from DNS it re transmits the query using TCP after 3 5 seconds of interval Considering the DNS uses TCP for Zone transfer and UDP for name and queries either regular primary or reverse UDP can be used to exchange small information whereas TCP must be
Why Dns Use Tcp And Udp

Why Dns Use Tcp And Udp
https://www.netburner.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/TCP-vs-UDP.png
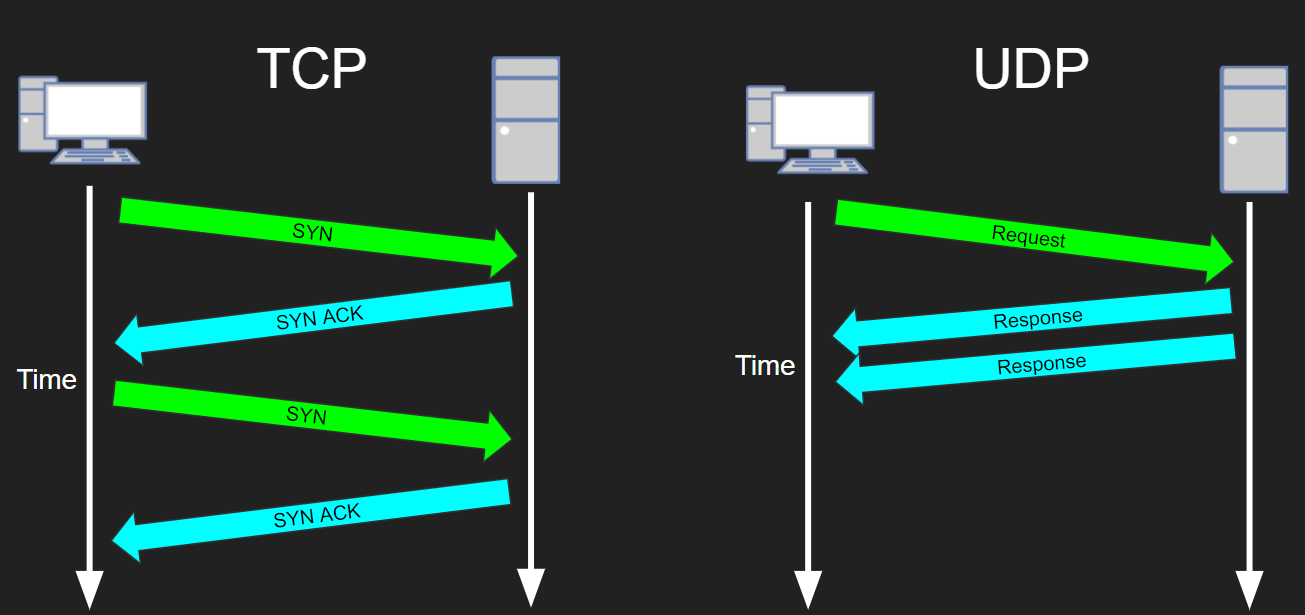
TCP IP Model A Level Computer Science
https://learnlearn.uk/alevelcs/wp-content/uploads/sites/20/2020/06/tcp-vs-udp.png
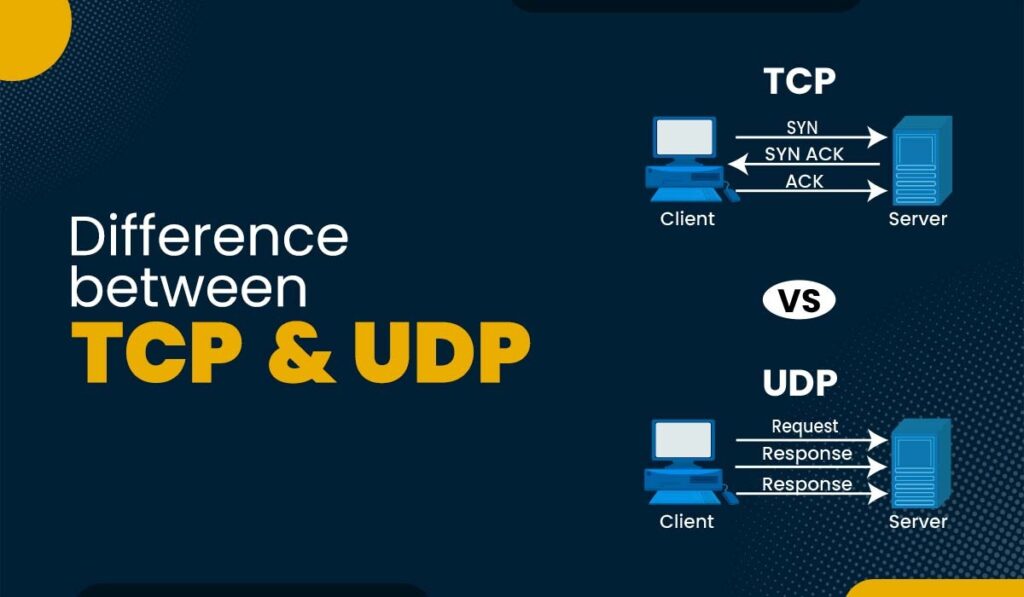
Tcp Vs Udp Comparison Differences Simple With Examples Ccna 200
https://www.pynetlabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/TCP-vs-UDP-1024x597.jpeg
Understanding when and why DNS uses UDP or TCP reveals the thoughtful engineering behind DNS functionality and performance DNS over UDP is the default DNS uses TCP when the size of the request or the response is greater than a single packet such as with responses that have many records or many IPv6 responses or most DNSSEC responses
In practice most DNS servers support both UDP and TCP though TCP is rarely used for simple DNS queries and is reserved mainly for operations like zone transfers The TCP is a connection oriented protocol whereas UDP is a connection less protocol DNS Servers need to maintain the same database between each other This is achieved by using Zone Transfer feature The
More picture related to Why Dns Use Tcp And Udp
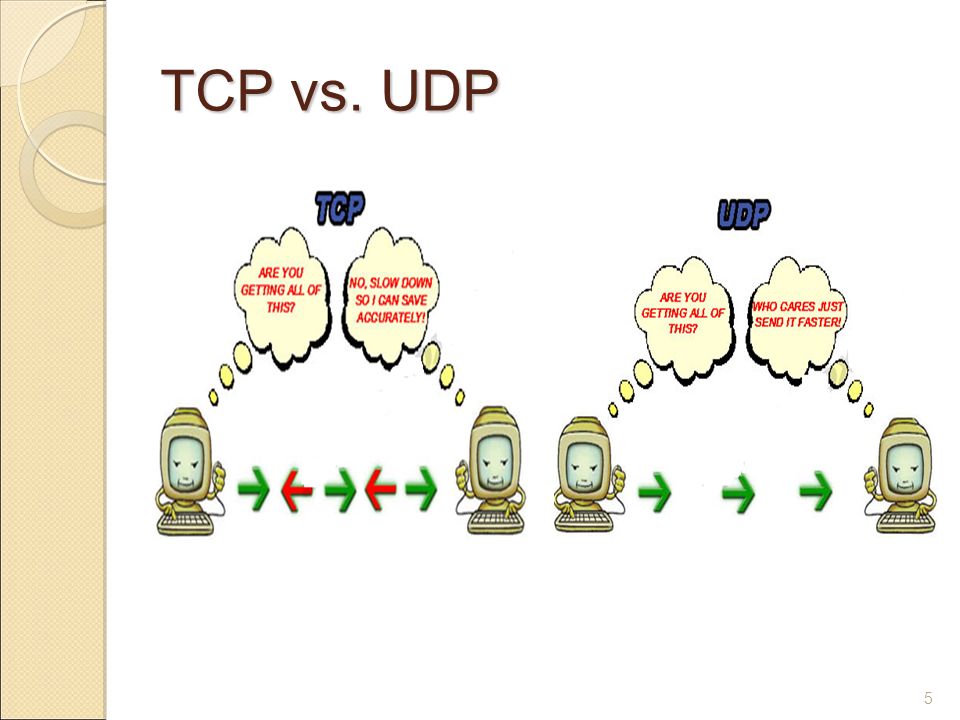
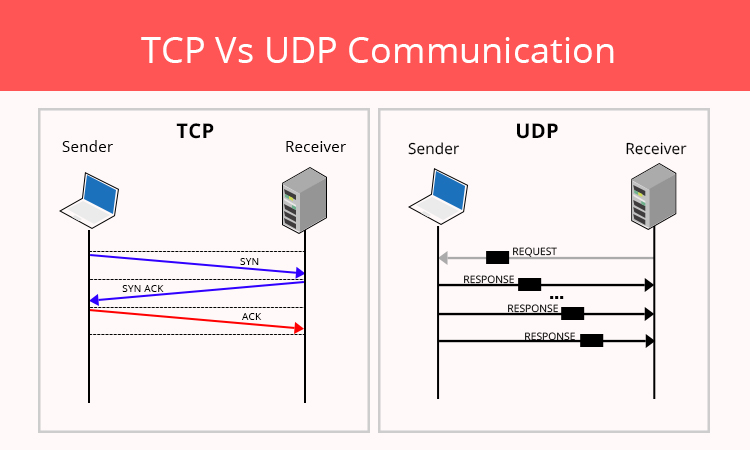
TCP Vs UDP Networking For Beginners With Debby
https://networkingforbeginners.weebly.com/uploads/9/0/6/4/90642157/tcpudp_orig.jpg

Ingin Tahu Perbedaan TCP Dan UDP Simak Artikel Berikut Ini PT
https://cdn.statically.io/img/nds.id/f=auto/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/TCP-dan-UDP.png
TCP Vs UDP What s The Difference Cloud4Y
https://www.cloud4y.ru/upload/medialibrary/b74/d97dkgfm5tu0ngqu8oirrev3ltj4rqql/TCP-i-UDP.jpeg
Why does DNS use UDP DNS works by using a complete set of tools and protocols UDP is one of them and it s key for DNS because UDP allows DNS to optimize its work while using it exclusively to send smaller data Why does DNS use TCP and UDP UDP can be used to exchange small information whereas TCP must be used to exchange information larger than 512 bytes To
DNS itself uses sometimes besides UDP as its primary protocol the reliable Transmission Control Protocol TCP too The last is used when the response data size By utilizing UDP DNS avoids the complexity associated with establishing and maintaining connections required by Transmission Control Protocol TCP This simplicity
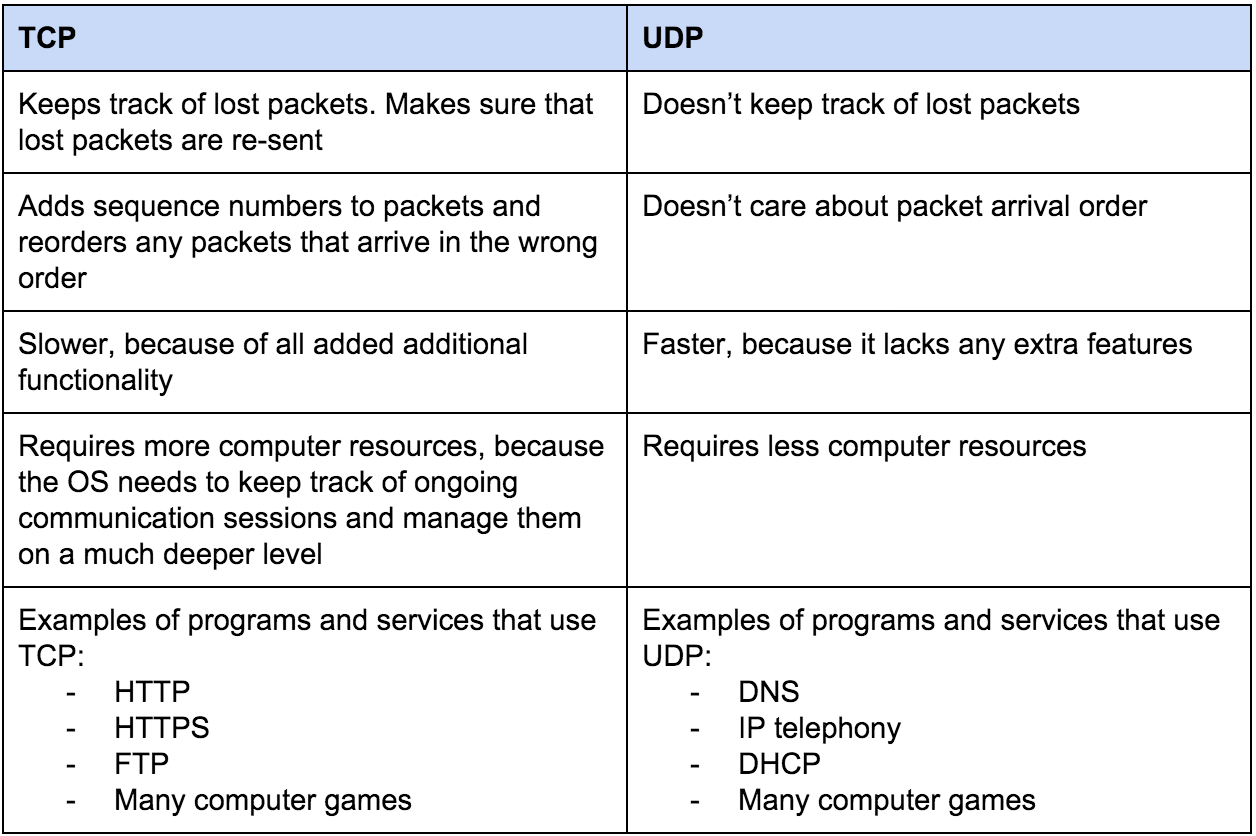
UDP And TCP Two Ways Of Sending Traffic Homenet Howto
http://www.homenethowto.com/wp-content/uploads/table-tcp-udp.png

Computer Science Difference Between UDP And TCP
https://2.bp.blogspot.com/-2dcCN6GQQvs/WrEsGjbOyiI/AAAAAAAAJuo/g--Mgsz0Vr4Ri7HbFtkInEiT_d82m2OZgCLcBGAs/s640/tcp-udp-transmission-control-protocol-and-user-datagram-protocol-12-638.jpg

https://www.techtarget.com › searchnetwork…
DNS uses both TCP and UDP ports to maintain consistent and reliable network performance TCP provides zone transfers while UDP handles name resolution queries and responses When managing network ports most

https://networkinterview.com › when-does-…
When a client doesn t receive a response from DNS it re transmits the query using TCP after 3 5 seconds of interval Considering the
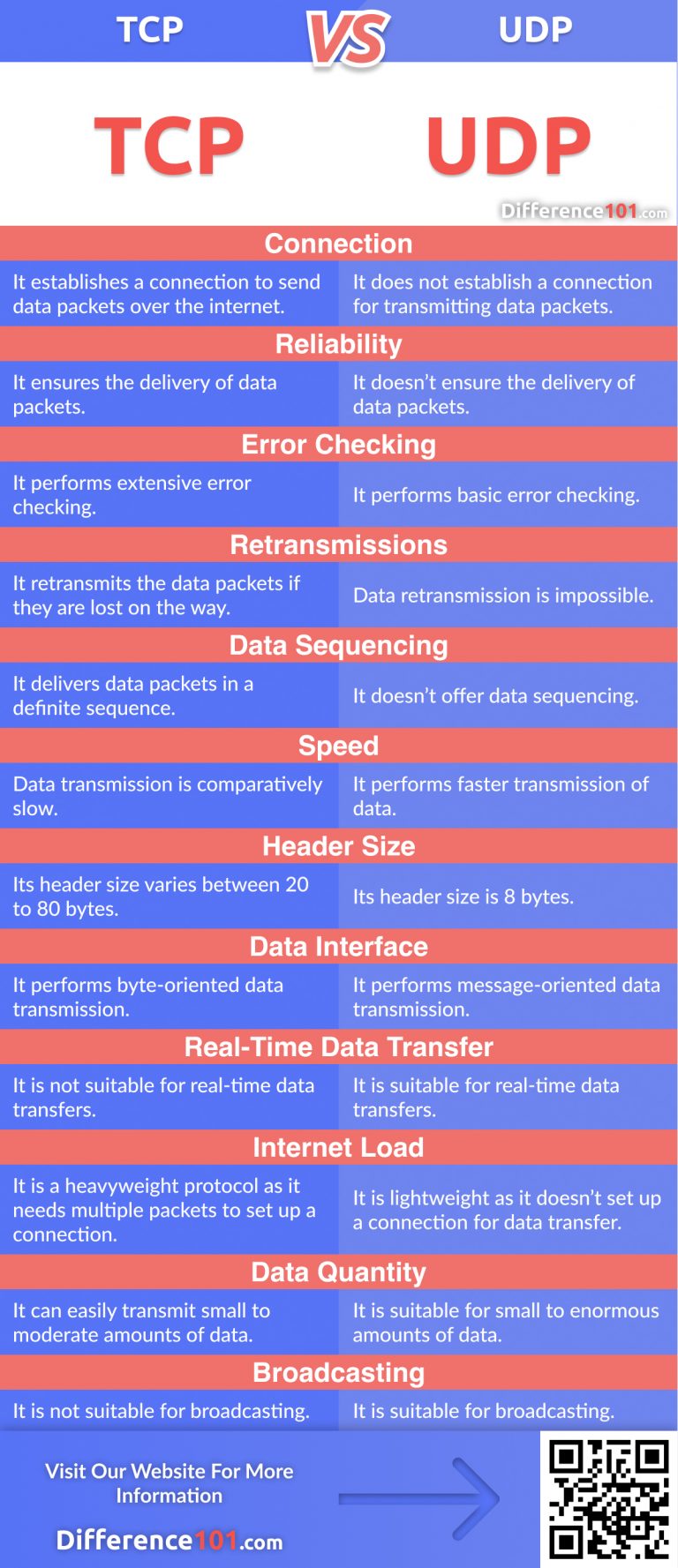
TCP Vs UDP Was Ist Der Unterschied Zwischen TCP Und UDP Difference 101

UDP And TCP Two Ways Of Sending Traffic Homenet Howto
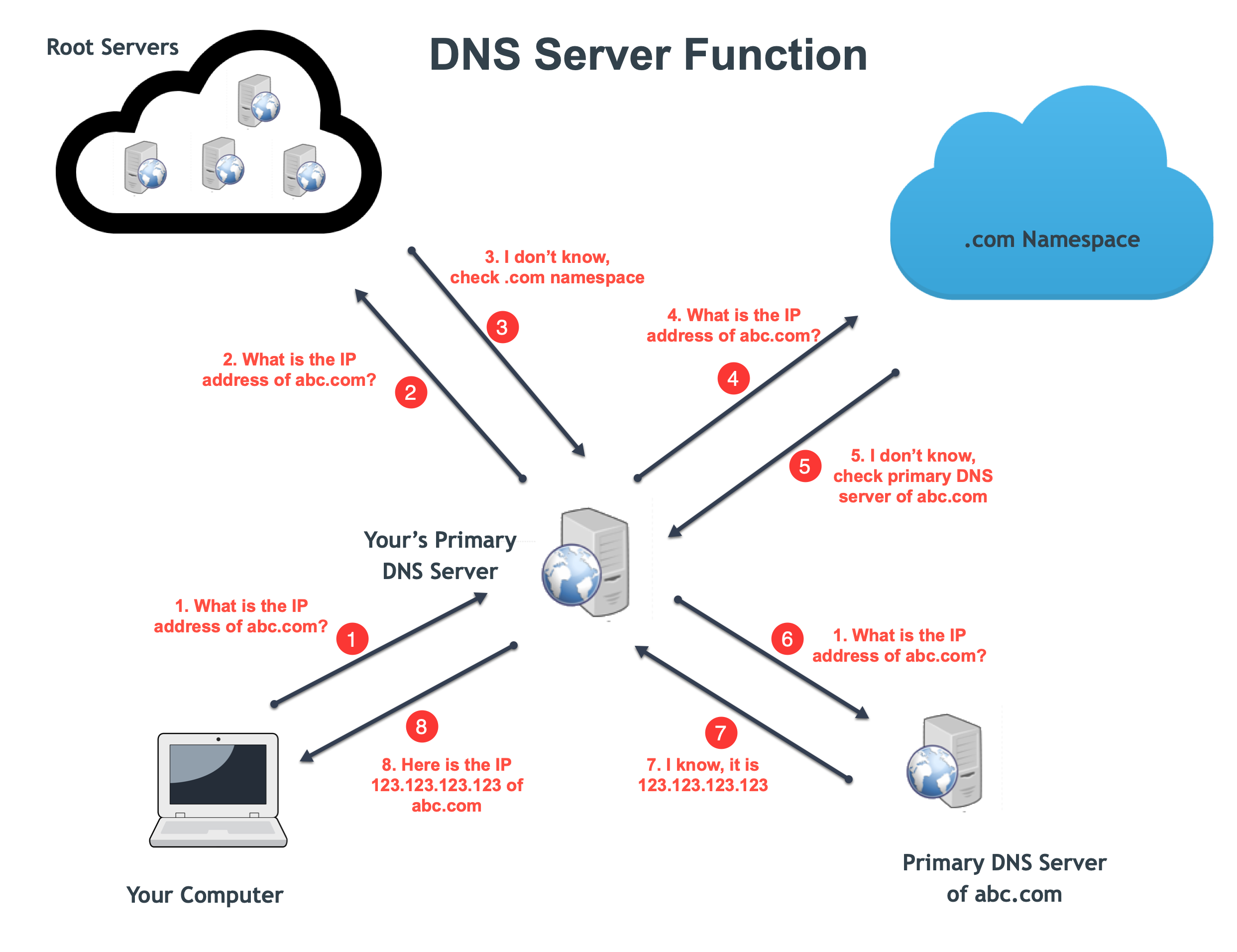
What Is DNS And How It Works WebNots
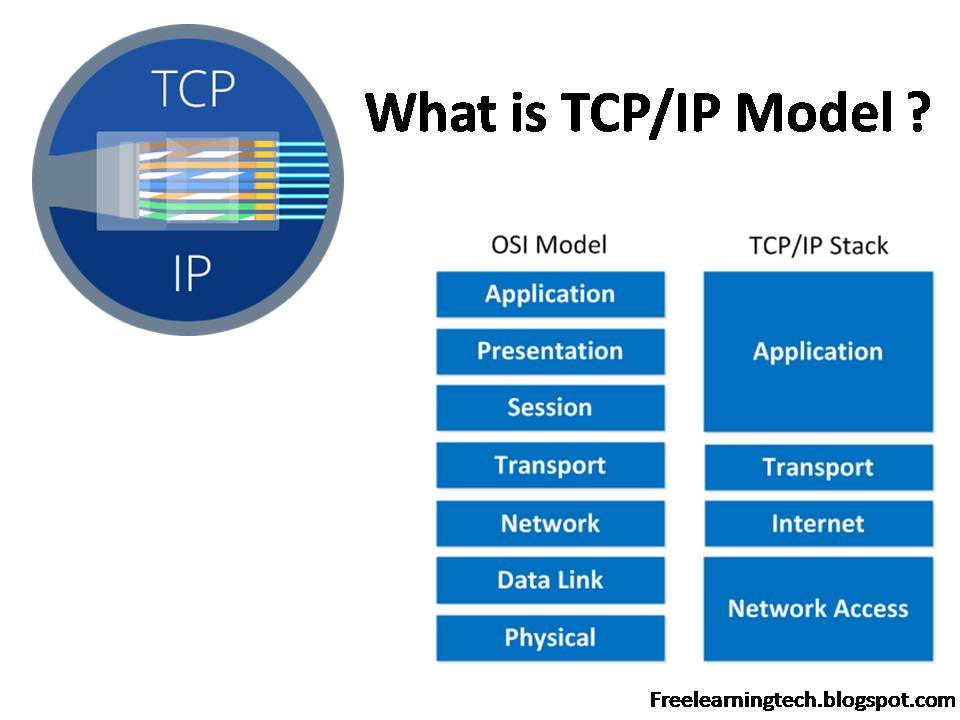
The Tcp Ip Model Diagram Following On From The Osi Networkin
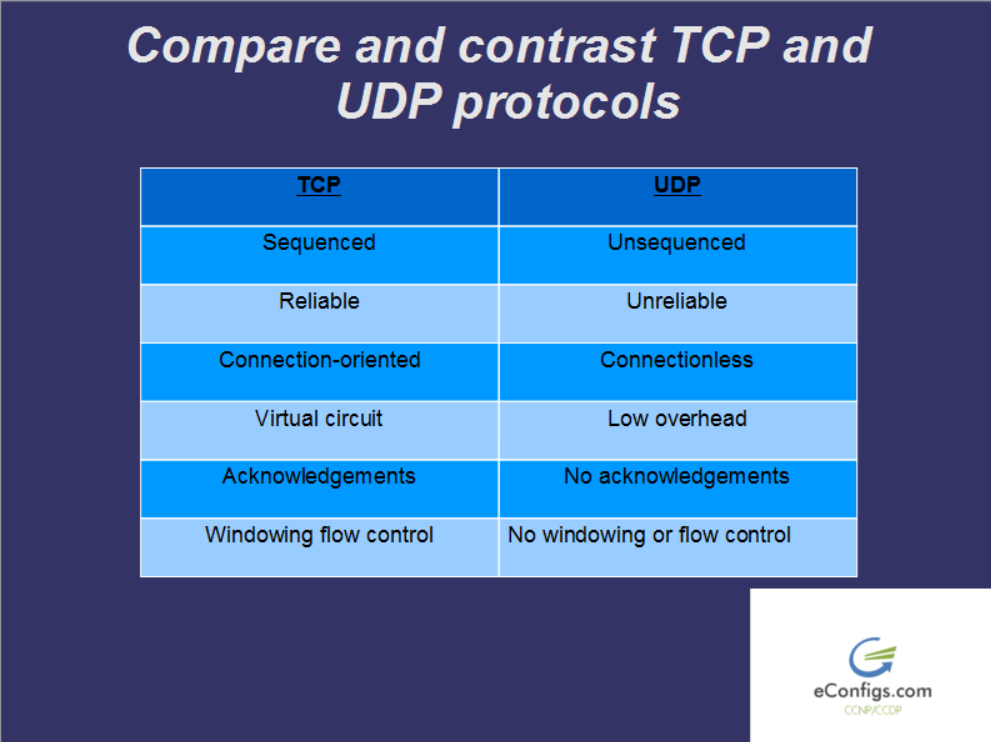
CCNA 1 2 Compare And Contrast TCP And UDP Protocols EConfigs

TCP Versus UDP

TCP Versus UDP

Why Does DNS Use UDP ClouDNS Blog
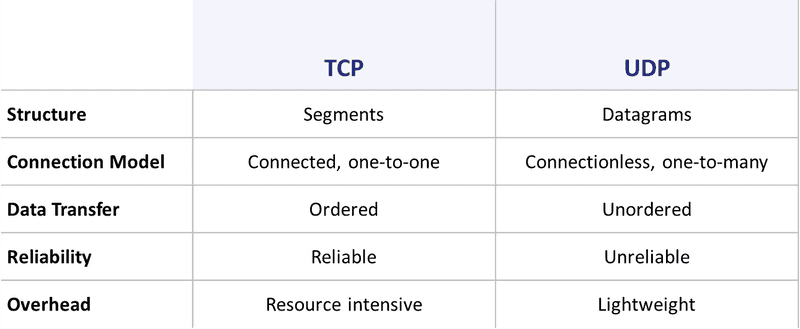
What Is The Difference Between Tcp And Udp Ports Infoupdate

TCP Vs UDP Protocol Key Differences Explained YouTube
Why Dns Use Tcp And Udp - DNS uses TCP when the size of the request or the response is greater than a single packet such as with responses that have many records or many IPv6 responses or most DNSSEC responses