The Antiderivative Of 1 Sin 2x Cos 2 X Is Learn to define what antiderivatives are Discover how to find the antiderivative of constants and power functions See antiderivative rules and
Some actually many functions do not admit an antiderivative expressible in this form it s the case of e x2 e x 2 and it can be proved although not easily When teaching the integration method of u substitution I like to emphasize its connection with the chain rule of integration Likewise the intimate connection between the product rule of derivati
The Antiderivative Of 1 Sin 2x Cos 2 X Is

The Antiderivative Of 1 Sin 2x Cos 2 X Is
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QDMsSLC4sQw/maxresdefault.jpg

Verify The Trigonometric Identity Cos pi 2 X sin x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DiS0MoX_ybM/maxresdefault.jpg
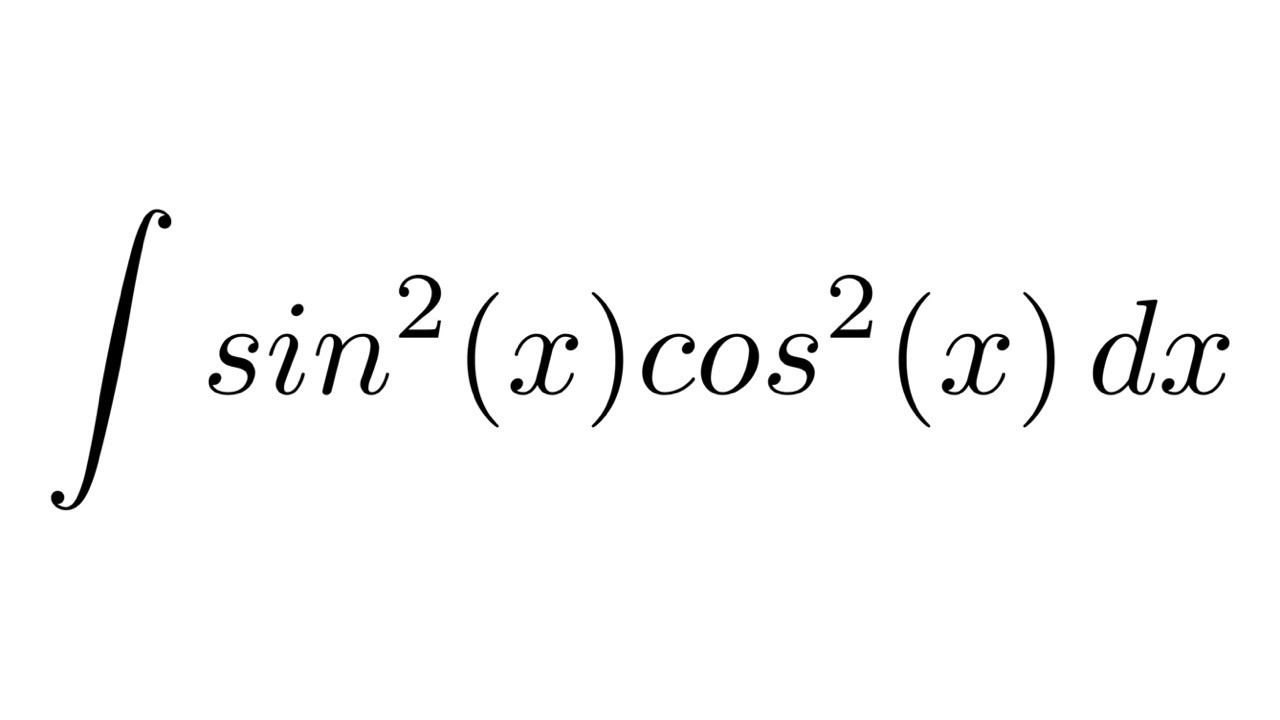
Integral Of Sin 2 x cos 2 x trigonometric Identities YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LBWbQfW4-PQ/maxresdefault.jpg
There are 2 potential questions here One is the question of why the definite Riemann integral gives the correct notion of area under a curve for a nonnegative Riemann You should know that this will always happen when solving for definite integral using the fundamental theorem of calculus no matter the antiderivative you find
As we know a non continuous function may have an antiderivative Thus the function may not be integrable That is although there is an explicitly defined antiderivative F x possibly not but I will prove that xx x x has no elementary antiderivative as many have claimed I will use Risch s decision semi algorithm for exponential polynomials in trascendental exponential extensions
More picture related to The Antiderivative Of 1 Sin 2x Cos 2 X Is
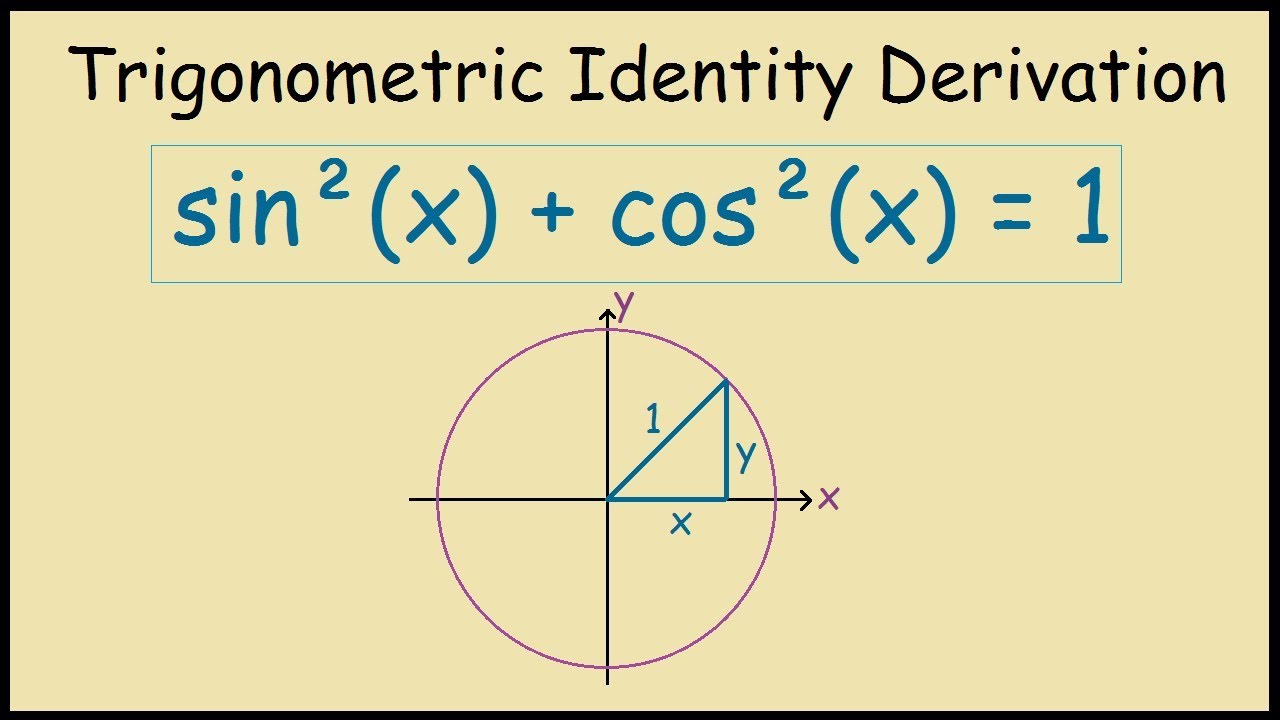
Sin 2 x Cos 2 x 1 Trig Identity Graphical Proof YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ILS9bS3svqo/maxresdefault.jpg

How To Integrate E 2x Integration Of E 2x Integral Of E 2x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/IFyAZq7ji24/maxresdefault.jpg

Derivative Of Sin x 2 Sin 2 x And Sin 2x With Chain Rule
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/hJVGumAnqL4/maxresdefault.jpg
This means that the antiderivative x y x y cannot be a polynomial or rational function since such functions are changed when you differentiate them So y x 1 x y x 1 x is then a If so I think I get what you want to say If a antiderivative f exists such that f z 1 z the value of the two integrals should be equal Does that have anything to do with the fact that Ln z isn t
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Trigonometric Identity With Double Angle Formula Sin2x Cos 54 OFF
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jYbt9fT9a00/maxresdefault.jpg
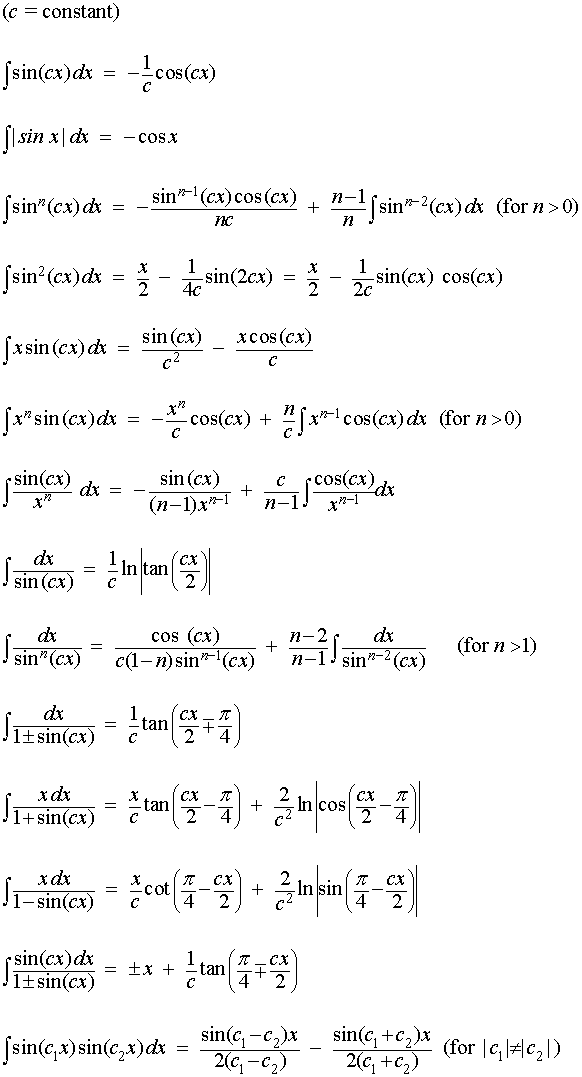
Ptupussy Blog
https://math.info/image/179/integral_sin.gif

https://study.com › academy › lesson › antiderivatives-of-constants-pow…
Learn to define what antiderivatives are Discover how to find the antiderivative of constants and power functions See antiderivative rules and

https://math.stackexchange.com › questions
Some actually many functions do not admit an antiderivative expressible in this form it s the case of e x2 e x 2 and it can be proved although not easily

Trigonometrical Identity Assignment Point

Trigonometric Identity With Double Angle Formula Sin2x Cos 54 OFF

sin 7x Sin X cos 5x Cos 3x Sin 2x Cos 2x Cot Xprove The
Solved For X Such That 0 The Expression sqrt 1 cos 2x sin X

Integrate
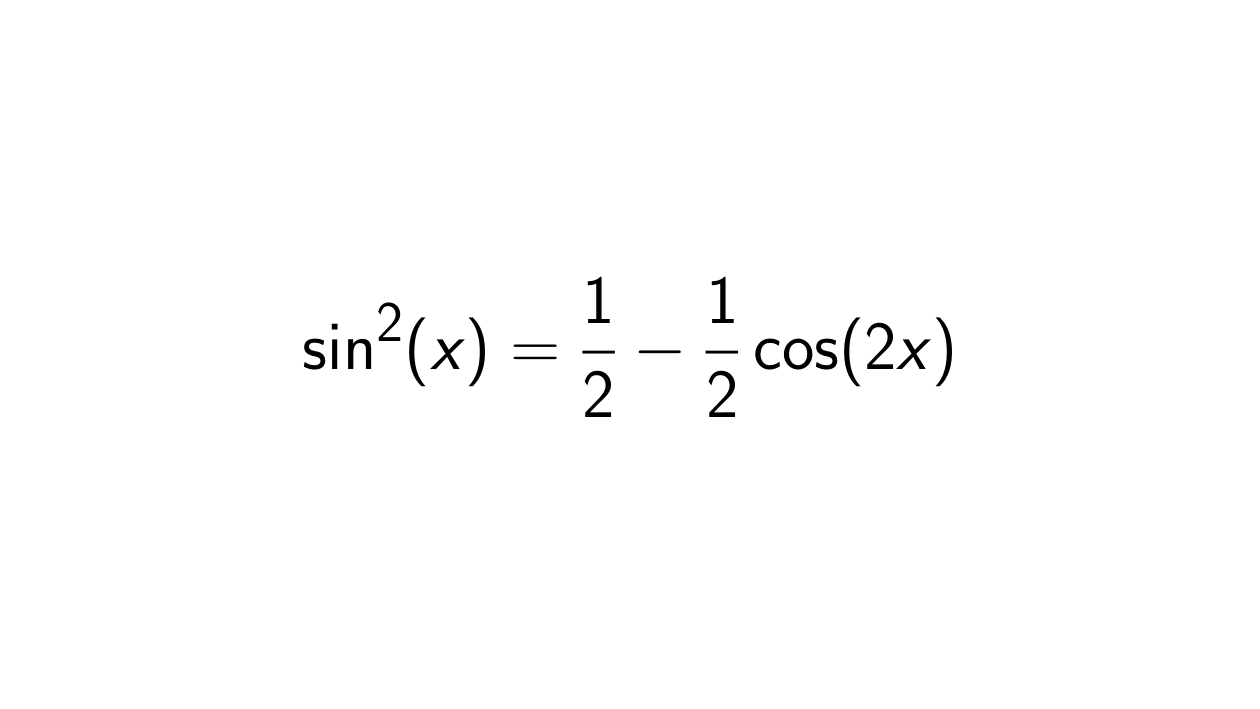
Mathematics
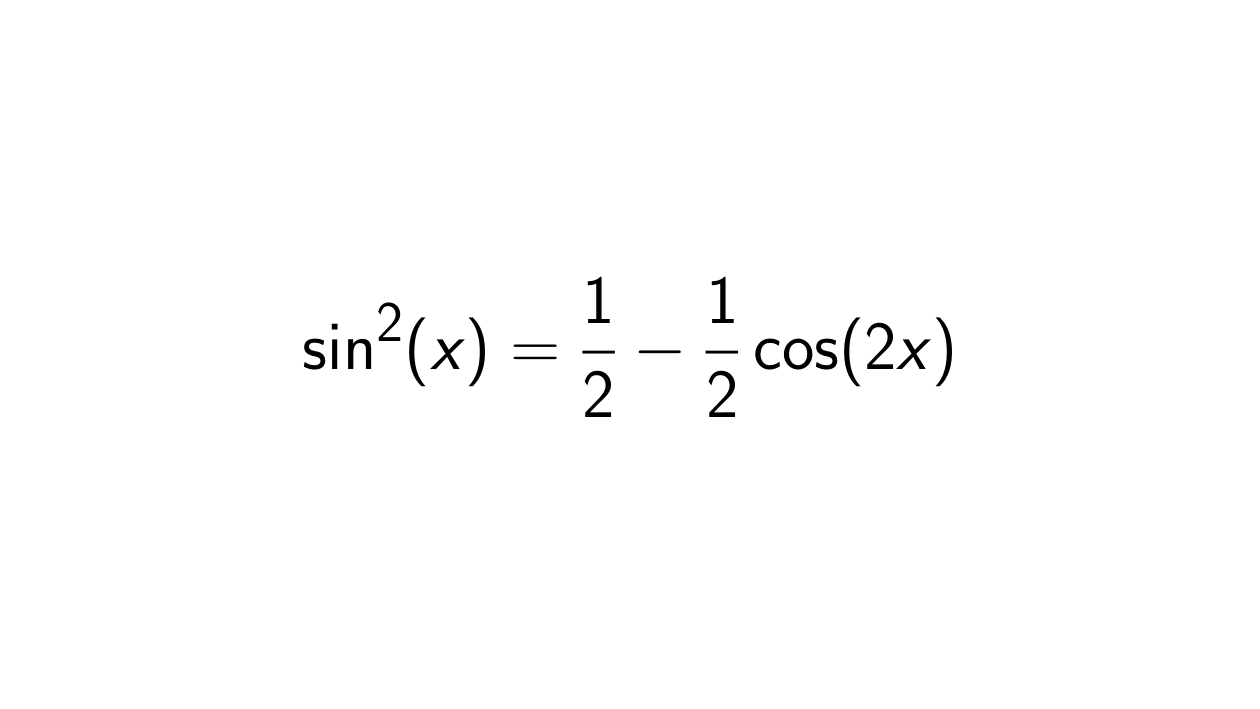
Mathematics
+%3D+sin(x2)+A.+–cos(x2)+B.+cos(x2).jpg)
Clicker Question 1 According To The FTC What Is The Definite Integral

1 cos Cos Top Sellers Www changeyourwindows

Ilectureonline
The Antiderivative Of 1 Sin 2x Cos 2 X Is - You should know that this will always happen when solving for definite integral using the fundamental theorem of calculus no matter the antiderivative you find