What Is Market In Economics Market a means by which the exchange of goods and services takes place as a result of buyers and sellers being in contact with one another either directly or through mediating agents or institutions Markets in the most literal and immediate sense are places in which things are bought and sold In the modern industrial system however the market is not a place it
In economics a market is a coordinating mechanism that uses prices to convey information among economic entities such as firms households and individuals to regulate production and distribution In his seminal 1937 article The Nature of the Firm Market for Intermediate Goods Such markets sell raw materials goods required for the final production of other goods Black Market A black market is a setup where illegal goods like drugs and weapons are sold Knowledge Market Knowledge market is a set up which deals in the exchange of information and knowledge based products
What Is Market In Economics

What Is Market In Economics
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OpowM0Z4RwU/maxresdefault.jpg

Market What It Means In Economics Types And Common 57 OFF
https://getuplearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/What-is-Market.jpg
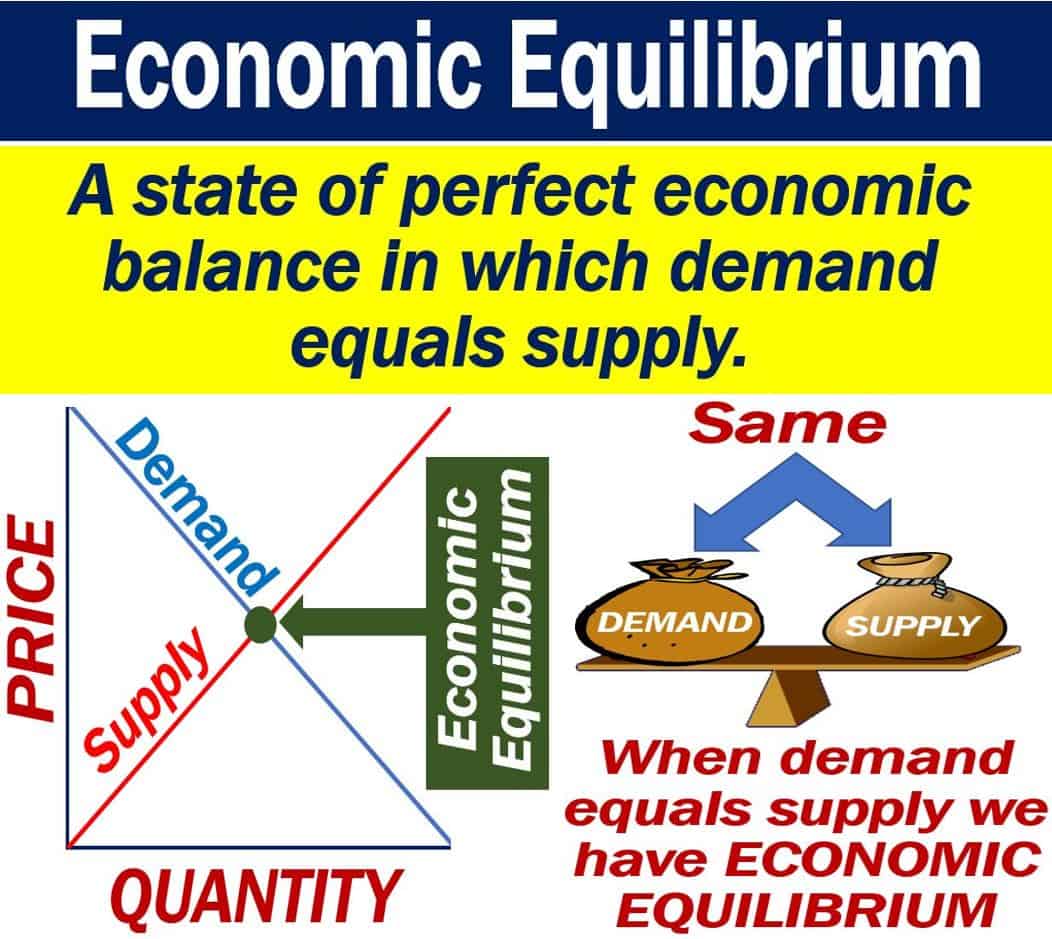
Equilibrium Price Definition Types Example And How To 55 OFF
https://marketbusinessnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Economic-Equilibrium.jpg
A market refers to a space that facilitates an economic transaction between parties the buyers and the sellers An economic transaction may involve an exchange of goods information services currency etc and does not necessarily involve legal tender A market is not necessarily a physical space such as a retail outlet In general terms Market refers to a particular place where buyers and sellers get together to purchase and sell goods WHAT IS MARKET IN ECONOMICS In economics the term market doesn t refer to any specific place but it refers to a
Therefore in a market economy there is a strong incentive for firms to be efficient cut costs and offer a good service to consumer 5 Consumer choice Without markets consumers would struggle to get the goods and services they need Markets enable consumers to choose the cheapest or best product leading to a greater range of choices Market in economics Market in Economics does not refer to a specific geographical area it refers to a platform for the exchange of a commodity or commodities Economists describe the term market as an arrangement where buyers and sellers come in close contact with one another either directly or indirectly to buy and sell goods or services or
More picture related to What Is Market In Economics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Economic-cycle-caf22d58aef949fcb919389e16db647a.jpg)
Stagflation
https://www.investopedia.com/thmb/jR00Qwv9WMaLtFVOMyAIEz1MaVQ=/1500x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Economic-cycle-caf22d58aef949fcb919389e16db647a.jpg

Activity Demand Shifters Resource Bank
https://microsite-sws-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/media/courseware/lesson/image/demand_MVt4Zpw.jpg
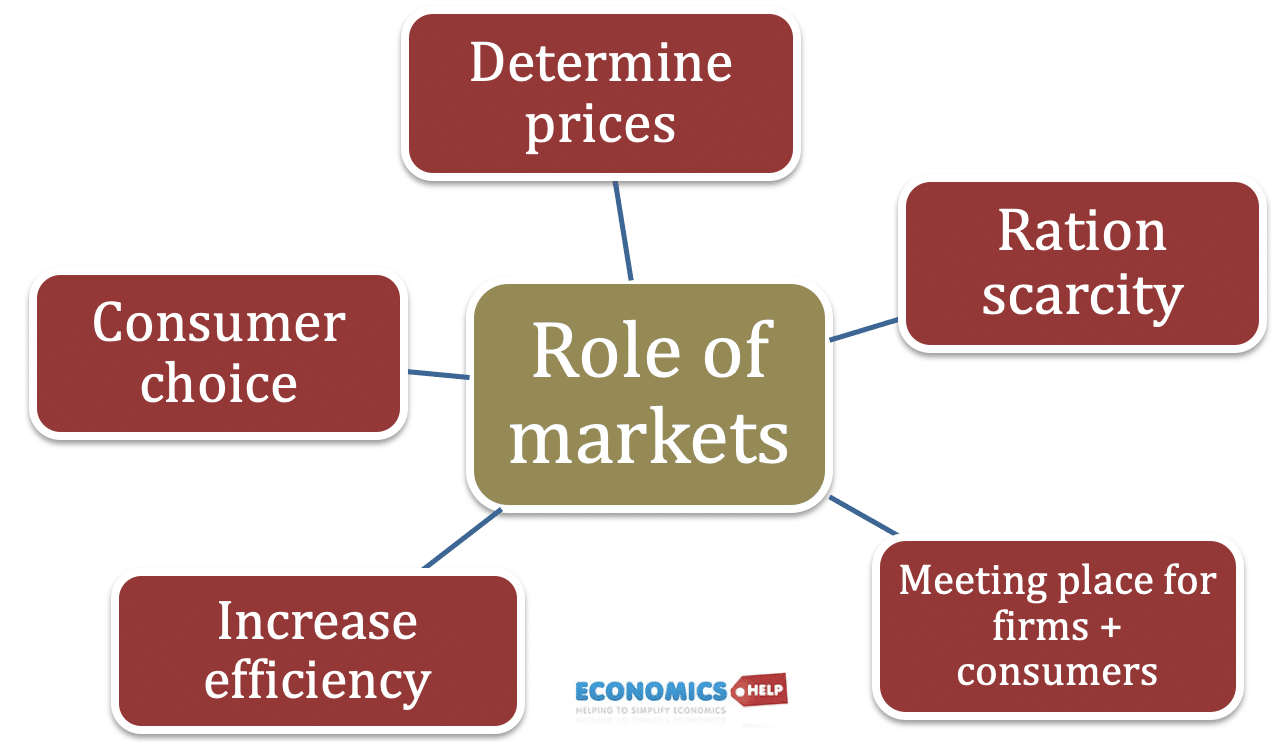
Market Stalls Economics Help
https://www.economicshelp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/role-of-markets.png
Economic Contexts Markets function in various economic systems such as market economies where prices are determined by supply and demand with little government control How Markets Work Markets facilitate the exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers driven by the principles of supply and demand which determine prices and A market economy is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is determined by supply and demand In a market economy interactions between consumers and businesses
[desc-10] [desc-11]
Subsidies Definitions Examples Analysis Evaluation
https://lh5.googleusercontent.com/cCo9Qncp14Y40yukT8VwkM4rECsU2waFpvHoDAA5zAZr3gl55raC1s3fdbfgH8IMH0ZxhiHZ9iSE5oT1e-YFwGLE2k-lKRGdG_Nm_bpJg5Wyp0oL-uZN9jHsTdARnANxg_xcJ66DoA_MmyBbdEICjQ

Supply And Demand
https://thumbs.dreamstime.com/z/supply-demand-balance-scale-economics-principles-law-words-gold-to-illustrate-principle-free-market-economy-38029279.jpg

https://www.britannica.com › money › market
Market a means by which the exchange of goods and services takes place as a result of buyers and sellers being in contact with one another either directly or through mediating agents or institutions Markets in the most literal and immediate sense are places in which things are bought and sold In the modern industrial system however the market is not a place it

https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Market_(economics)
In economics a market is a coordinating mechanism that uses prices to convey information among economic entities such as firms households and individuals to regulate production and distribution In his seminal 1937 article The Nature of the Firm

Difference Between Business Economics And Economics Business And
Subsidies Definitions Examples Analysis Evaluation
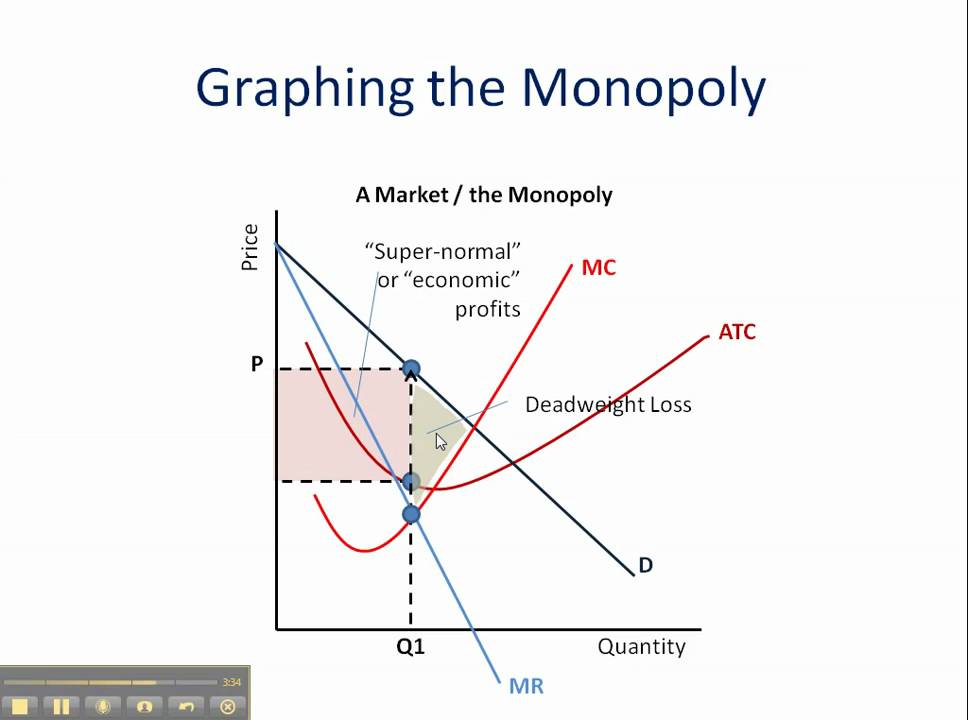
Monopoly How To Graph It YouTube

Lasermyte Blog

Market Equilibrium Graph Homecare24

MARKET ECONOMY Leveraged Growth

MARKET ECONOMY Leveraged Growth
Concentrated Marketing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Perfect-Competition-2de51ba3fa8a40e9bdfdc7b98a195ce0.png)
Perfect Competition Examples And How It Works 59 OFF

Equilibrium Biology Simple
What Is Market In Economics - [desc-12]